Wind power
Introduction
This form of renewable energy derives from when wind has been used to power wind turbines and has been used for centuries.
How this energy is collected
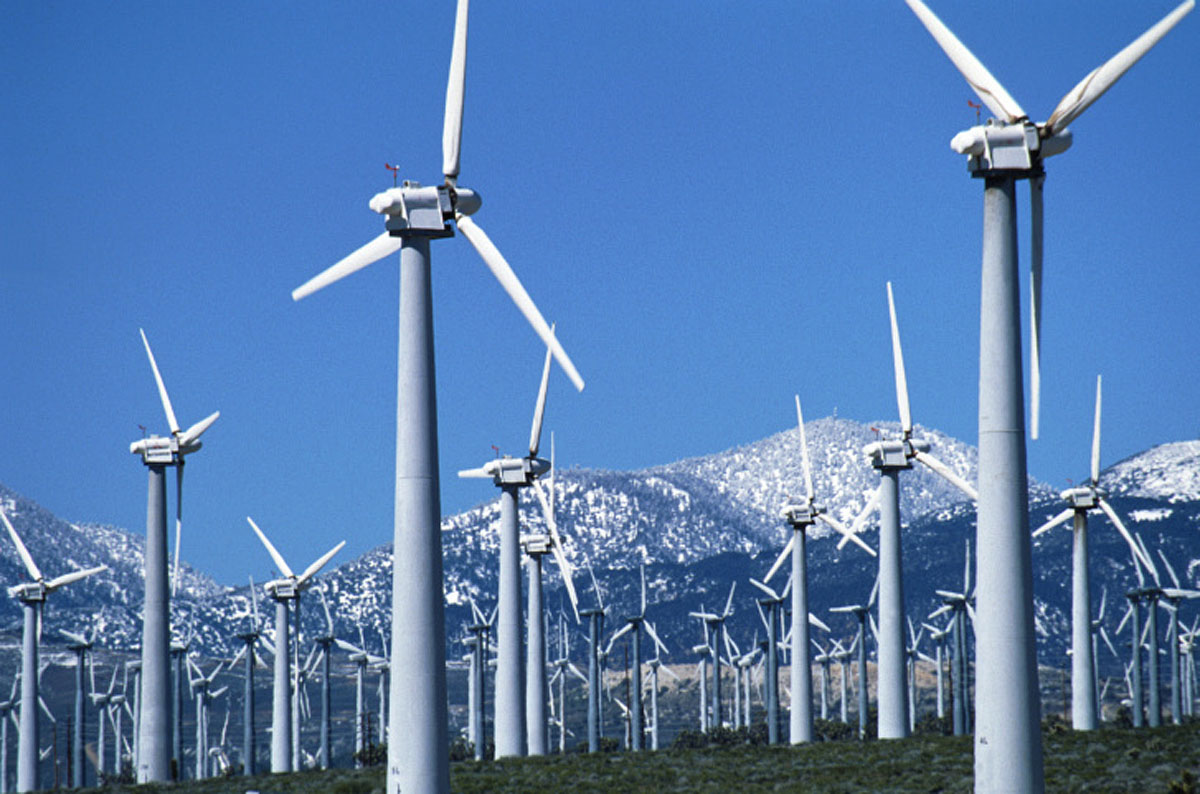
The way that it is collected these days is by large wind turbines and they are collected in wind farms. They are usually places in areas that generate a reasonable and consistent amount of strong winds, and are usually large areas of flat land or those near the coast that are subject to prevailing winds. There are two types of turbines that can be used to generate electricity, the first being a vertical axis turbine which is the older and more commonly used and the second type is a horizontal axis turbine, which is actually more efficient because it doesn’t have to be pointed into the wind for it to be effective.
Benefits
A benefit to using this type of renewable energy is that it is both non-polluting and freely available in many different areas. Another way that they are becoming more beneficial is that they are becoming a lot more efficient and the cost of the electricity that they are generating is falling. There are further economic benefits to using wind power and that is that wind power currently account for 2.5% of worldwide power and growing at approximately 25% per annum. Furthermore, the cost of production of a wind farm is actually similar to the production cost of a new coal and gas installations.
The downsides to using this type of energy is that to be efficient approximately 20 turbines need to be used together in the form a wind farm and these can be unsightly and noisy, and in turn they need to be in close proximity to populations so the electricity can be distributed. Another key disadvantage to this type of energy source is that winds are intermittent and do not blow all the time. However, this can be mitigated by having power management techniques such as having excess capacity storage, or reducing the demand when production is low.
If you require consultancy services or further information please click here.